March
14th,
2017
1. 概念
Trie树,又叫字典树、前缀树(Prefix Tree)、单词查找树或键树。
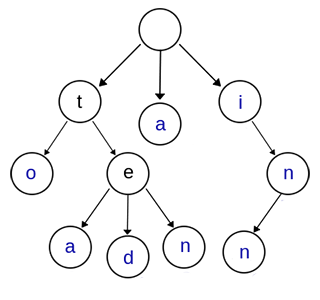
上图是一棵Trie树,表示了关键字集合{“a”, “to”, “tea”, “ted”, “ten”, “i”, “in”, “inn”} 。
Trie树的基本性质:
- 根节点不包含字符,除根节点外的每一个子节点都包含一个字符。
- 从根节点到某一个节点,路径上经过的字符连接起来,为该节点对应的字符串。
- 每个节点的所有子节点包含的字符互不相同。
2. Trie树的优缺点
Trie树的核心思想是空间换时间,利用字符串的公共前缀来减少无谓的字符串比较以达到提高查询效率的目的。
优点
- 插入和查询的效率很高,都为
O(m),其中m是待插入/查询的字符串的长度。 - 不同于hash,Trie树中不同的关键字不会产生冲突。
- Trie树可以对关键字按字典序排序。
3. Trie树的应用
- 字符串检索
- 词频统计
- 相比hash, trie树可以压缩空间
- 字符串排序
- 前缀匹配
4. Trie树的实现
from collections import defaultdict
class TrieNode(object):
def __init__(self):
self.children = defaultdict(TrieNode)
self.is_word = False
# self.word = None
class Trie(object):
def __init__(self):
self.root = TrieNode()
def insert(self, word):
current = self.root
for letter in word:
current = current.children[letter]
current.is_word = True
# current.word = word
def search(self, word):
current = self.root
for letter in word:
current = current.children.get(letter)
if not current:
return False
return current.is_word
def startsWith(self, prefix):
current = self.root
for letter in prefix:
current = current.children.get(letter)
if not current:
return False
return True
class TrieNode {
public char val;
public boolean isWord;
public TrieNode[] children = new TrieNode[26];
public TrieNode() {}
public TrieNode(char c){
val = c;
}
}
public class Trie {
private TrieNode root;
public Trie() {
root = new TrieNode();
root.val = ' ';
}
public void insert(String word) {
TrieNode current = root;
for(int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++){
char c = word.charAt(i);
if(current.children[c - 'a'] == null){
current.children[c - 'a'] = new TrieNode(c);
}
current = current.children[c - 'a'];
}
current.isWord = true;
}
public boolean search(String word) {
TrieNode current = root;
for(int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++){
char c = word.charAt(i);
if(current.children[c - 'a'] == null) return false;
current = current.children[c - 'a'];
}
return current.isWord;
}
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
TrieNode current = root;
for(int i = 0; i < prefix.length(); i++){
char c = prefix.charAt(i);
if(current.children[c - 'a'] == null) return false;
current = current.children[c - 'a'];
}
return true;
}
}
class TrieNode{
public:
char val;
int weight;
TrieNode *children[26];
TrieNode() {}
TrieNode(char c){
val = c;
}
~TrieNode();
};
class Trie {
private:
TrieNode* root;
public:
Trie() { root = new TrieNode(' '); }
void insert(string word, int weight) {
TrieNode* current = root;
for(int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++){
char c = word[i];
if(!current->children[c - 'a']){
current->children[c - 'a'] = new TrieNode(c);
}
current = current->children[c - 'a'];
}
current->weight = weight;
}
TrieNode* startsWith(string prefix) {
TrieNode* current = root;
for(int i = 0; i < prefix.length(); i++){
char c = prefix[i];
if(!current->children[c - 'a']) return nullptr;
current = current->children[c - 'a'];
}
return current;
}
}